
86 755 2523 4088

service@agccert.com


86 755 2523 4088

service@agccert.com

 Release Time:2021-08-23
Release Time:2021-08-23
Summary of energy efficiency in Japan
Japan's energy conservation law ,it is stipulates that more than 30 categories of products are required to meet the requirements of the energy conservation law. For most product categories, Only voluntary statements and manufacturer's test reports are required. Among them, LED products must be tested in a registered testing laboratory in Japan.
Top Runner Program mandatory
The Energy-saving Labelling Program(voluntary)
Those meeting the requirements of the energy efficiency standard are green, those failing to meet the energy efficiency standard are orange, and the star unified energy-saving label appeared in 2005.

Top Runner Program(mandatory)
In order to promote energy-efficient machines and appliances products, the law on the rational use of energy (hereinafter referred to as the energy conservation law) requires manufacturers and importers to ensure that their products meet the target standards of energy conservation. When Japan revised the law on rational use of energy for the third time in 1998, they added a very important energy-saving management measure "top runner program", which was implemented in 1999. The program is committed to continuously improving the energy conversion and performance standards of the latest products“ The leader standard adopted by the leader plan is different from the minimum energy efficiency standard. It sets the maximum energy efficiency level in the current market as the energy efficiency target value of the product. When the target year reaches, the new target energy efficiency value will be reset. Manufacturers are given some flexibility, and products below the target energy efficiency value can still be sold on the market“ The products involved in the "leader program" mainly focus on the continuous growth of energy consumption in housing, commerce and transportation, and focus on improving the energy efficiency of machinery and equipment.
(The energy-saving standards of equipment in various fields in Japan are mainly based on the leader standard, which is mainly composed of six parts: product range (differentiation), target year, target benchmark value (energy efficiency limit value), measurement / measurement method, determination method of benchmark value achievement rate and identification. The product scope and type are determined by the energy consumption, usage, relevant testing standards, testing capacity and other factors. The target year is determined on the basis of full consideration of energy consumption and energy efficiency level, social demand, product development cycle, investment and construction cycle of facilities and equipment and future development prospect of high-efficiency and energy-saving technology. The target year on different types products can be different, which is generally set as 4 ~ 8 years. The target benchmark or limit value is determined by the product classification according to the current maximum energy efficiency value and the improvement potential of energy efficiency level. It can be a numerical value or a non numerical calculation formula.)
(The "leader" standard is voluntary, but if the difference between manufacturers and importers of the products and the "leader" standard is too large, the The Ministry of economy, industry and trade (METI) of Japan will take measures to intervene, including reviewing and providing improvement suggestions. The manufacturer must comply with METI's recommendations, otherwise it will be punished by warnings, announcements, orders, and even fines.
(The 23 products covered by the "leader plan" include 9 kinds of household appliances: air conditioner, refrigerator, freezer, electric rice cooker, microwave oven, gas cooking appliance, gas water heater, fuel water heater and heat pump water heater. Next, take the refrigerator as an example to introduce the benchmark provisions of Japan's "leader" plan.)
(The refrigerator in the "leader" plan is applicable to the refrigerator covered by JISC9801:2006 characteristics and test methods of household refrigeration appliances, but does not include the following refrigerators:)
(Absorption refrigerator;)
Refrigerator of Peltier method (special for hotels, etc.)
Motor vehicle refrigerator)
Commercial refrigerator)
For freezers (freezers), motor vehicle loaded freezers and commercial freezers are not included)
The energy efficiency value (annual power consumption) of refrigerators and freezers sold in Japan after April 1, 2010 shall not be greater than the energy efficiency limits in Table 1 and table 2:
Table 1 benchmark values of energy efficiency of refrigerators (including refrigerators) from 2010)
Category | Refrigeration mode | Rated internal volume | Number of refrigerator doors | Calculation formula of target reference value |
A | Natural convection type | - | - | E=0.844×Vadj+155 |
B | Forced circulation type | ≤300L | - | E=0.774×Vadj+220 |
C | >300L | Single door | E=0.302×Vadj+343 | |
D | Multi door | E=0.296×Vadj+374 |
Table 2 benchmark value of energy efficiency of freezer since 2010
Category | Refrigeration mode | Rated internal volume | Number of refrigerator doors | Calculation formula of target reference value |
E | Natural convection type | - | - | E=0.844×Vadj+155 |
F | Forced circulation type | ≤300L | - | E=0.774×Vadj+220 |
G | >300L | E=0.302×Vadj+343 |
Table 3 benchmark values of energy efficiency of refrigerators since 2016
Category | Refrigerator type | Shape | Inverter controlled motor | Calculation formula of target reference value |
1A | Freezer | vertical | yes | E3=0.345V3+86nR+64dR+315 |
1B | no | E3=0.766V3+86nR+64dR+106 | ||
1C | horizontal | - | E3=1.12V3+70nR+34dR+237 | |
2A | Refrigerated freezer | vertical | - | E3=0.872V3+86nR+64dR+186nF+295dF-113 |
2B | horizontal | - | E3=2.43V3+70nR+34dR+157nF+157dF-183 |
Table 4 benchmark value of energy efficiency of freezer since 2016
Category | Calculation formula of target reference value | |
Category | Shape | |
3A | vertical | E3=1.96V3+186 nF+295dF+788 |
3B | horizontal | E3=4.12V3+157 nF+157dF+349 |
4A | Top sliding door type | E3=1.16V3+211 |
4B | Top glass sliding door | E3=1.39V3+359 |
(Among that E is the reference energy efficiency (kWh / year), V3 is the adjusted internal volume (L), D is the external dimension (mm) specified in JIS B 8630:2009, NR is the number of non designed central columns for the double doors of the refrigeration room, NF is the number of non designed central columns for the double doors of the refrigeration room, Dr is the multi door index of the refrigeration room, and DF is the multi door index of the refrigeration room.)
Mandatory energy saving labels for electrical retailers
In April 2006, Japan revised the energy conservation law. In October of the same year, TV sets, air conditioners and refrigerators began to implement the energy conservation label plan for electrical retailers, forcing electrical retailers to provide unified new energy conservation labels. The energy-saving label of electrical appliance retailers provides information such as energy-saving grade, energy-saving logo, expected annual energy consumption and power cost. The energy-saving label is a comparison mark, which is composed of one to five stars (multi-level evaluation system), so that consumers can see the energy efficiency grade of products at a glance, which is convenient for consumers to adopt energy-efficient products. The label also shows the cost of electricity or energy used by consumers to buy electricity every year.
(The selection principle of target products is to meet the following three conditions: ① it belongs to "leader" products; ② Mainly for household use; ③ There is a calculation method of annual energy cost. At present, there are 19 kinds of products, including 9 kinds of household appliances, such as air conditioner, refrigerator, freezer, electric rice cooker, microwave oven, stove, gas cooking appliance, gas water heater and oil water heater.)
Products meeting the following conditions can be included in the category of multi-level evaluation system:
1. Electrical appliances belonging to the "leader" program;
2 Electrical appliances belonging to the energy-saving label plan;
3 To be used for household purposes;)
4 The energy cosumption of the product is very high;)
5 According to the design method of multi-level evaluation standards, the compliance rate of energy-saving standards of each category varies by more than 5%. At present, only five products meet the multi-level evaluation system, including air conditioners and refrigerators. For these energy consuming equipment, due to the large difference in energy-saving performance of each equipment, the energy efficiency indicators marked on the energy efficiency label and the annual power cost are different. Therefore, the Japan Energy Conservation Center (ECCJ) establishes a label combining mandatory energy conservation label and multi-level evaluation system, and the simple version without multi-level evaluation system shall not be used for these two products, and the star representing multi-level evaluation must be marked on the label.)
Taking the refrigerator as an example, the star rating (multi-stage evaluation and grading) of the refrigerator is shown in the following table:
Achievement rate of multi-stage evaluation energy efficiency benchmark)
★★★★★ Benchmark achievement rate > 198%
★★★★ 165% < benchmark achievement rate £ 198%
★★★ Benchmark achievement rate £ 165%
★★ Benchmark achievement rate: £ 133%
★ Benchmark achievement rate £ 100%
(The retailer mandatory energy-saving label of refrigerator is shown in the figure below. The label gives information such as multi-stage evaluation grade (star), benchmark achievement rate, annual power consumption and estimated annual power charge.)

The Energy-saving Labelling Program
The products with voluntary energy-saving labels must be the target products of the "leader", especially the household appliances used by ordinary consumers. So far, it has been designated as the product with energy-saving label requirements, including 9 kinds of household appliances: air conditioner, refrigerator, freezer, electric rice cooker, microwave oven, stove, gas cooking appliance and gas heater. These 9 kinds of household appliances need to publish their energy-saving product information on the website of Japan Energy Conservation Center (ECCJ. Voluntary energy-saving labels, energy-saving signs, compliance rate of energy-saving standards, target annual and annual power consumption to achieve energy-saving standards. Failure to meet the energy-saving standard is indicated in orange.
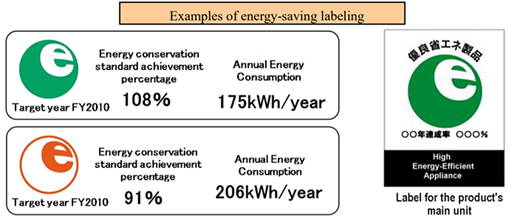
The energy saving label contains the following information:
(1) Energy saving signs: products with energy efficiency standards of more than 100% are green signs, and products with energy efficiency standards of less than 100% are orange signs, so as to encourage green sign products with high performance;)
(2) Energy saving standard compliance rate: We use % to represent the compliance rate of the energy efficiency standard (target value) of the product. The higher the compliance rate, the energy saving performance of the product.)
(3)Annual power consumption: the annual power consumption of the product calculated by a specific test method;)
(4) Target year for achieving energy-saving standards: during the period of reaching the target of energy-saving standards, set the energy-saving standards for each product according to the energy-saving law.)
(In short, the energy-saving label is not only required to be green, but also the greater the compliance rate of energy-saving standards, the higher the energy-saving performance and the lower the energy consumption. If you want to use energy-efficient products for a long time, you should not only consider the function and price of the products, but also choose products marked with electricity bill or power consumption.)
