
86 755 2523 4088

service@agccert.com


86 755 2523 4088

service@agccert.com

 Release Time:2021-12-06
Release Time:2021-12-06 Textile fiber is the fine substance with a diameter of several micrometers to several tens of micrometers,
Textile fiber is the fine substance with a diameter of several micrometers to several tens of micrometers, and a length that is many times larger than the diameter, at least 1,000 times larger, and has a certain degree of flexibility and strength. Textile fibers can be divided into two categories: natural fibers and chemical fibers. The specific classifications are as follows:

Common natural fibers include cotton, flax, ramie, silk, wool, etc.;
Common chemical fibers include polyester, nylon, spandex, acrylic, viscose and so on.
Importance of textile product fiber composition identification
From the above fiber classification, we clearly know that there are many types of textile fibers, and different fibers also have differences in cost. The difference between some fibers can even reach hundreds of times. Therefore, the raw materials of textile products are different, and there are also price differences when they are sold. The labeling of fiber composition and content can allow consumers to understand the raw material composition of the product most intuitively, fully protect the rights and interests of consumers, and prevent unscrupulous merchants from deceiving consumers with shoddy products. At the same time, consumers can clarify the performance, scope of application, and use of the product according to the type and content of fiber.
Textile fiber identification
At present, most countries and regions have issued regulations or standards that require that the textile products sold must indicate the fiber composition and content on their labels. For textile testing, fiber content testing is an important test item in textile testing, and it is also an important means to verify the correctness of product fiber component labels. In fiber content detection, it is first necessary to identify which type of fiber it is, and then the specific content of each fiber can be further analyzed. Below we introduce the identification of textile fibers
Textile fiber identification is based on the physical and chemical properties of the fiber, using different analysis methods to test, by comparing standard photos, standard pictures and standard data to identify unknown fibers
Textile fiber identification method standard
FZ/T 01057.1 General Instructions
FZ/T 01057.2 Combustion method
FZ/T 01057.3 Microscopy method
FZ/T 01057.4 dissolution method
FZ/T 01057.5 Color reaction method containing chlorine and nitrogen
FZ/T 01057.6 melting point method
FZ/T 01057.7 density gradient method
FZ/T 01057.8 infrared spectroscopy
FZ/T 01057.9 birefringence method
AATCC TM 20
ISO/TR 11827
Commonly used identification methods are combustion method, microscope method, and dissolution method
Combustion method: According to the state of the fiber when it is close to the flame, in contact with the flame, and when it leaves the flame, as well as the smell produced during combustion and the characteristics of the residue after combustion, the types of fibers are distinguished. The combustion characteristics of common fibers are shown in Table 1:
Table 1 Combustion characteristics of common fibers
Fiber name | Burning state | ||||
Close to the flame | Contact flame | Leave the flame | odor | Residue characteristics | |
cotton | Does not shrink or melt | Burning quickly | Keep burning, | Burnt paper flavor | It is thin and soft gray-black flocculent |
numb | Does not shrink or melt | Burning quickly | Yellow flame | Burnt paper flavor | It is thin and soft grayish white flocculent |
silk | shrink | Curl, melt, burn | Keep burning, | Singeing | Loose and crisp black particles |
wool | shrink | Curl, melt, burn | Yellow flame | Singeing | Loose and brittle black coke-like |
Viscose fiber | Does not shrink or melt | Burning quickly | Burns slowly, sometimes goes out on its own | Burnt paper flavor | It is thin and soft gray-black flocculent |
Polyester | Meltdown | Melt, burn, melt first and then burn, with solution dripping | Burns slowly, sometimes goes out on its own | Special aromatic sweetness | Glassy dark brown hard ball |
Nylon | Meltdown | Melt, burn, melt first and then burn, with solution dripping | Keep burning, | Ammonia smell | Glassy dark brown round beads |
Spandex | Meltdown | Melting, burning | Yellow flame | Peculiar smell | White gelatinous |
Acrylic | Shrinkage | Micro melting, burning, bright sparks | Can prolong combustion and emit black smoke | Spicy | Black irregular beads, fragile |
Microscopic method: Observe the longitudinal shape and cross-sectional shape of the fiber with a microscope, or cooperate with dyeing, dissolving and other methods to distinguish natural fibers from chemical fibers.
Common fiber morphology characteristics
cotton:
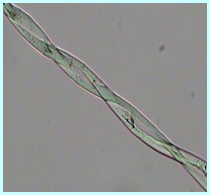
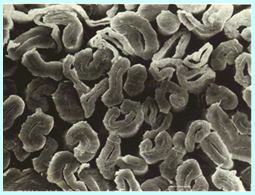
Longitudinal: flat ribbon with natural twist Horizontal: round waist with middle cavity
Ramie Fiber
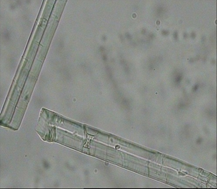

Longitudinal: The fiber is thicker and has a long shape Horizontal: round waist, with middle cavity stripes and bamboo-like horizontal joints
Flax fiber
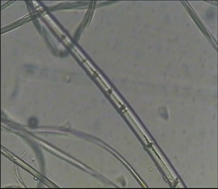
Longitudinal: The fiber is thin, with bamboo-like horizontal nodes Lateral: polygonal, with cavity
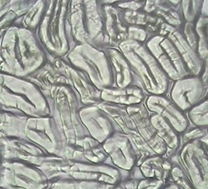
Wool fiber
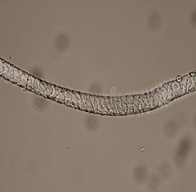
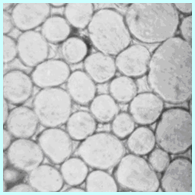
Longitudinal: rough surface, scaly Horizontal: round or approximately round
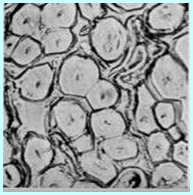
Viscose fiber
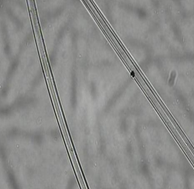
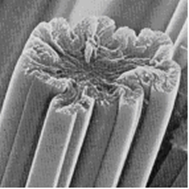
Longitudinal: smooth, grooved Horizontal: zigzag shape, with skin-core structure
Polyester
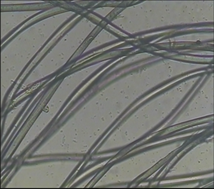

Longitudinal: smooth, with black spots Horizontal: round
Nylon
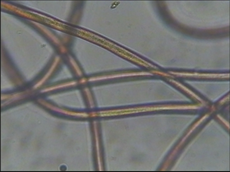 -
-
Longitudinal: smooth, with black spots Horizontal: round
Chemical dissolution method: the use of different fibers in different solvents has different solubility, which is a more commonly used method and can also be quantitatively determined. It is suitable for various textile materials, including dyed fibers, yarns and fabrics with mixed components.
Common fiber dissolving performance table
Fiber name | hydrochloric acid 20% 24℃ | hydrochloric acid 37% 24℃ | Sulfuric acid 75% 24℃ | Sodium hydroxide 5% boiled | Formic acid 85% 24℃ | glacial acetic acid 24℃ | M-cresol 24℃ | Dimethyl formamide 24℃ | Xylene 24℃ |
Polyester | I | I | I | I | I | I | S 93°C | I | I |
Nylon | S | S | S | I | S | I | S | I | I |
Acrylic | I | I | SS | I | I | I | I | S 93°C | I |
Vinylon | S | S | S | I | S | I | S | I | I |
Polypropylene | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | S |
Spandex | I | I | P | I | I | P | I | S 93°C | I |
In the table, S—dissolved; SS—slightly soluble; P—partially dissolved; I—not dissolved.
Summary of fiber identification:
In actual identification, it is difficult to identify some samples using a single method. It is necessary to use several methods comprehensively and analyze them systematically to accurately identify fibers. details as follows:
First of all, the unknown sample fiber can be slightly sorted. If it is not an elastic fiber, the fiber can be preliminarily divided into three categories: cellulose fiber, protein fiber and synthetic fiber by using the combustion test method;
Cellulosic fibers and protein fibers have their own different longitudinal and lateral morphological characteristics, which can be identified by microscopy; synthetic fibers generally use chemical dissolution methods according to the fiber dissolution performance table, that is, according to the dissolution characteristics of different chemical reagents at different temperatures. Identify. For polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, and polyvinylidene chloride, chlorine detection method and melting point method can also be used for verification.
At present, all kinds of electronic products that are indisp...
New energy vehicles is the car to use the power source which...
Electric Portable Bikes and battery test standards
In recent years, energy storage and power battery technologi...
Hardness is the ability of a material to resist being presse...


Does the article solve your problem